Got hurt? Don’t worry, apply an antiseptic cream and phew and you’ll be done! But, what if the injury is major? Like bitten by an animal or something like that? We all are aware that we need to take T.T (Tetanus Toxoid) injection. Similarly, we use vaccines to prevent various diseases, which include intradermal vaccines too.
An intradermal injection is given into the dermis, just below the epidermis (layers of skin). This route has the longest absorption time as compared to subcutaneous injections and intramuscular injections.
Not only for vaccines, but also for many tests (blood tests), blood donations etc. We need to take injections. Ever wondered how many types of syringes do we have? This type of basic knowledge is useful in our daily-life, even if we do not belong to the medical field.
Let us discuss about Syringes And Needles.
Right syringe, right needle and the right part of the body should be used for a particular medication.
Syringe:
The syringe is nothing but a tube with a nozzle with a piston for sucking in and ejecting the liquid in a thin stream, which is then used for body cavities or cleaning wounds, or are fitted with a hollow needle for injecting or withdrawing fluids.
According to the World Health Organization, about 90% of the medical syringes are used to administer drugs, 5% for vaccinations and 5% for other uses such as blood transfusions.
The various uses of syringe includes:
- Injecting medicines into the body is step one.
- Into the bloodstream intravenous treatment
- Applying substances such as glue or lubricants
Previously, syringes were formed of metal or glass and had to be cleaned and sterilised before being used again, but now medications are given using plastic and disposable syringes.
Types of syringes:
Based on the syringe tip syringes are classified as Luer-Lok or Non-Luer-Lok syringes. The Luer-Lok syringes have tips such that the needles that can be twisted and locked into the place can be fitted in these tips whereas Non-Luer-Lok tips require needles that can be pressed on to the tip without being twisted into place.
BD Luer-Lok:
These are use where a secure connection with another device is require. The tip is thread for a ‘locking’ fit.
Luer Slip Tip:
A friction-fit connection, this will ensure a connection that is likely to detach.
Eccentric Luer Slip Tip:
Generally used for venipunctures and aspiration of fluids that requires closeness to the skin.
Catheter Tip:
These are used for cleaning catheters, gastrostomy tubes, and other devices.
Syringes come in a number of sizes, ranging from 0.5ml to 60ml. Medication to intravenous lines and irrigate wounds require larger syringes.
The second classification consists of:
1) Insulin Syringes.
2) Tuberculin Syringes.
Insulin Syringes:
1) Small in size, hold between 0.3 and 1 ml of medication.
2) Calibrated in units (mostly up to 100 units).
3) Designed for self injection.
4) Used to give subcutaneous injection.
Tuberculin Syringe:
1. Small in size, hold up to 1 ml of fluid
2. Calibrated in millimeters.
3. Has a long thin barrel with a pre-attached needle used for tuberculosis testing.
4. Injected right into the skin (intradermal vaccine).
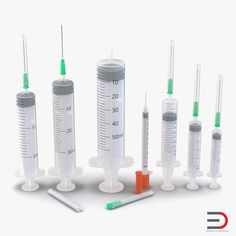
SYRINGES AND NEEDLES
Source: Pinterest
Let us discuss another part in the anatomy of syringe i.e., injection needle. Needles are makeup of stainless steel to avoid their rusting. The needle is hollow with a hole in the middle.
Anatomy of needle
1) Hub: fits onto the tip of the syringe.
2) Shaft: a long length of the needle.
3) Bevel: the slanted tip of the needle (creates a hole in the skin)
Long- beveled tips reduce discomfort when it pierces the skin.
Types of injection needles:
Needles are mainly differentiate on the basis of length and diameter.
Length range: ½ inch-3 inches.
Diameter range: 7 gauge-33 gauge.
As the needle gauge gets bigger, the needle’s diameter gets smaller.
We should also know that two different needles may have the same length and have different gauge sizes.
Gauge selection is based on:
1) Concentration of medication given.
2) Body size and age of an individual.
3) Mobility status of the patient.
4) Required absorption rate for medication.
Long needles are use for intramuscular medications and shorter needles for subcutaneous medications.
1. Intravenous needle:
Inserted into the vein of a person.
2. Safety needles:
These are use nowadays in almost all medical setting, to reduce the risk of the patient getting stuck with an infect needle.
3. Winged needle:
It is also name as a butterfly needle, hold by its wings and attach to a slender, flexible catheter line. Various needles commonly utilized with injections gauges in relation to their colors.
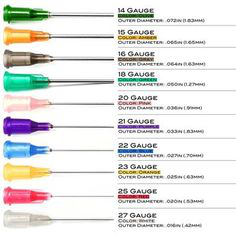
Source: Pinterest
The very first thing which should be kept in mind before purchasing a syringe or needle is its Size. The size must be considered foremost. Make sure the syringe’s size corresponds to the volume of medications to be administered as well as the desired pressure flow. If you’re planning to provide huge amounts of medication, you’ll need a large syringe. The same can be said of low-pressure flow. However, there are different criteria for purchasing a syringe and needle. Some of them are listed below:
- The syringe size is determined by the amount of medication to be administered.
- The syringe hub is determined by the type of needle hub utilised. (Catheter Tip, Luer Lock, Slip Tip, Eccentric Tip)
- The needle gauge is determined by the viscosity of the medicine.
- The needle gauge and length are determined by the injection site.
So, it is very important to know these criteria and purchase a syringe or needle that best caters your needs.
So, now I hope you are well aware of the intradermal vaccine, types of Syringes And Needles and you don’t remain alien to all these on your next visit to the doctor. Be Aware, Stay safe, Stay healthy.
